DDR5 vs DDR4 Performance, Efficiency, and Benchmarks Compared: The Definitive Guide for Smart Builders
Navigating the world of PC components can feel like stepping onto a rapidly moving conveyor belt. Just when you get comfortable with one generation, the next one rolls in, promising groundbreaking advancements. This is precisely the scenario facing PC enthusiasts and everyday users alike when it comes to RAM: the showdown between DDR5 vs. DDR4. Are these new modules truly a game-changer for performance, efficiency, and future-proofing, or is DDR4 still holding its own in the benchmark battles?
It's a critical question for anyone building a new system or considering an upgrade. Your choice of memory impacts everything from gaming frame rates to video rendering speeds and even the snappiness of your daily multitasking. As a seasoned journalist who's seen countless hardware cycles, I'm here to cut through the marketing noise and give you the unvarnished truth, empowering you to make the most informed decision for your setup and your wallet.
At a Glance: Key Takeaways on DDR5 vs. DDR4
- DDR5 is the Future: Offers significantly higher bandwidth, increased capacity, and improved power efficiency. It includes innovations like on-die ECC and a dual-channel architecture per DIMM.
- Performance Leaps (But Not Everywhere): DDR5 brings much higher theoretical bandwidth. In real-world gaming, the FPS difference might be marginal in many titles, becoming more noticeable in CPU-bound scenarios or with specialized CPUs like AMD's 3D V-Cache models.
- Compatibility is Key: DDR5 is not backward compatible with DDR4 motherboards. You need a compatible CPU and motherboard (e.g., AMD Ryzen 7000 Series with AM5 socket) to use it.
- Pricing Approaching Parity: While DDR5 was initially much pricier, it's now closing the gap, especially for popular speeds like 6000 MT/s. DDR4 remains more cost-effective for budget or mid-range builds.
- Future-Proofing Value: DDR5 platforms are here to stay, supporting upcoming features like AI acceleration and high-bandwidth workloads. Investing in DDR5 now can offer better long-term compatibility for future hardware and software.
- Your Needs Dictate: The best choice depends heavily on your current hardware, budget, and specific performance goals rather than simply chasing the latest trend.
The Dawn of a New Era: What Sets DDR5 Apart?
When we talk about DDR5, we're not just discussing a minor iteration; it's a fundamental architectural shift in how memory operates. DDR5, or Double Data Rate 5, is the latest generation of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM), a direct successor to DDR4. But what does that really mean for your system?
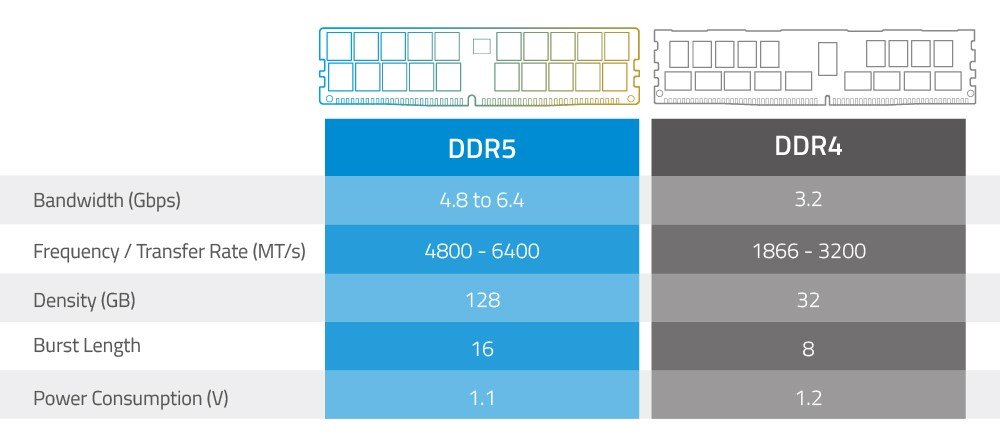
Imagine your computer's memory as a highway for data. DDR4 was a respectable multi-lane highway, but DDR5 has expanded it, adding more lanes and increasing the speed limit. This translates to significantly higher bandwidth, meaning more data can move between your CPU and RAM simultaneously. Where DDR4 typically topped out around 3200-3600 MT/s (mega transfers per second), DDR5 starts at 4800 MT/s and scales much higher, with readily available kits reaching 6000 MT/s and beyond.
Beyond raw speed, DDR5 brings a suite of innovations designed for the demands of modern computing. It offers increased capacity per module, allowing for denser sticks (e.g., 32GB or 48GB per DIMM are becoming common) which is crucial for professional workstations or content creators dealing with massive files. Crucially, DDR5 also boasts improved power efficiency, operating at a lower voltage (1.1V compared to DDR4's 1.2V). This might seem minor, but it contributes to lower power consumption and heat generation across the entire system.
One of the less visible but equally impactful innovations is on-die ECC (Error Correction Code). While not full-blown server-grade ECC (which often requires specific CPU and motherboard support), on-die ECC helps detect and correct single-bit errors within the DRAM chips themselves before data even leaves the module. This translates to greater data integrity and system stability, a silent guardian against potential crashes or corruption, especially important for intense, long-duration workloads.
Another clever trick up DDR5's sleeve is its dual-channel architecture per DIMM. Unlike DDR4, where each memory stick (DIMM) functions as a single 64-bit channel, DDR5 DIMMs are internally split into two independent 32-bit channels. This might sound counter-intuitive, but it allows for more parallel operations and better access efficiency, even with fewer physical DIMMs installed. It's like having two smaller, faster delivery trucks instead of one larger, slower one.
For anyone keen to understand the deeper technical aspects of this leap in memory technology, it's fascinating to Explore the 5th generation Ram and its core advancements.
Raw Power Under the Hood: Performance Benchmarks That Matter
So, what do these technical advancements mean for real-world usage? This is where the rubber meets the road, and the story of DDR5 performance is nuanced.
Gaming Performance: A Subtle Edge
For many gamers, the most burning question is, "Will DDR5 boost my FPS significantly?" The answer, often, is "it depends." In a GPU-bound scenario—which describes most gaming at higher resolutions and settings—the difference in average FPS between a well-tuned DDR4-3600 kit and a speedy DDR5-6000 kit is frequently marginal. You might see a 5-10% improvement, sometimes less, across a range of popular titles. This is because the graphics card is working at its maximum, and faster RAM isn't the primary bottleneck.
However, the picture changes in CPU-bound scenarios. These are situations where your CPU is struggling to keep up, often seen in games with complex AI, large open worlds, high player counts, or when aiming for extremely high frame rates (e.g., 240Hz+ monitors in esports titles). In these cases, faster DDR5 can provide a more noticeable uplift, as the CPU can fetch and process data from memory more quickly.
The biggest gaming performance gains for DDR5 are often observed with specific CPU architectures, notably AMD's 3D V-Cache CPUs like the Ryzen 7800X3D. These CPUs feature a large L3 cache that significantly reduces memory latency. When paired with faster DDR5, the combination can unlock substantial frame rate improvements, as the CPU can more effectively utilize both its massive cache and the high-speed memory. For such specialized builds, DDR5 becomes a clear performance enhancer.
Productivity and Content Creation: Where DDR5 Shines
Beyond gaming, DDR5 truly flexes its muscles in memory-intensive applications. If you're a content creator, running multiple demanding applications simultaneously, or working with large datasets, DDR5's higher bandwidth and increased capacity make a tangible difference:
- Video Editing: Applications like Adobe Premiere Pro or DaVinci Resolve benefit from faster memory when scrubbing through timelines, rendering effects, or exporting high-resolution footage. The ability to load larger segments of video into RAM reduces reliance on slower storage.
- 3D Rendering and CAD: Design software such as Blender, AutoCAD, or SolidWorks often juggles immense models and textures. DDR5 allows for quicker loading of these assets and faster processing during renders, translating directly into saved time.
- Heavy Multitasking: Running a virtual machine, having dozens of browser tabs open, streaming, and editing photos simultaneously will stress your memory. DDR5's efficiency and higher capacity mean your system remains snappier, with fewer slowdowns or stuttering.
- Data Science and Machine Learning: Workloads involving large datasets and complex algorithms can be heavily bottlenecked by memory bandwidth. DDR5 provides a significant boost, accelerating training times and data processing.
In these professional scenarios, the gains aren't just about raw speed but also about the overall responsiveness and stability of your system, allowing you to focus on your work rather than waiting for your computer.
The Compatibility Conundrum: Can Your System Handle DDR5?
This is perhaps the most crucial point to understand: DDR5 RAM is not backward compatible with DDR4 motherboards. You cannot simply swap out your old DDR4 sticks for new DDR5 modules. The physical notch on the DIMM (memory stick) is in a different location, preventing accidental insertion into an incompatible slot. More importantly, the electrical signaling and voltage requirements are entirely different.
To use DDR5, you absolutely need a compatible CPU and motherboard. As of late 2023 and into 2024, this primarily means:
- AMD Platforms: The AMD Ryzen 7000 Series processors (e.g., Ryzen 7 7800X3D, Ryzen 9 7950X) on the AM5 socket require DDR5 memory. Compatible motherboards include those with B650 or X670 chipsets. If you're building an AM5 system, DDR5 is your only option.
- Intel Platforms: Intel's 12th, 13th, and 14th generation Core processors (e.g., Core i9-12900K, i7-13700K, i5-14600K) on the LGA 1700 socket offer a unique choice. Many motherboards for these platforms (e.g., Z690, Z790) come in either a DDR4 or a DDR5 variant. You must purchase a motherboard specifically designed for the type of RAM you intend to use. You cannot use both DDR4 and DDR5 on the same motherboard.
What if you have an older platform?
If your current PC is running an older Intel platform (11th Gen or older) or an older AMD platform (AM4 socket, like Ryzen 5000 Series), then you are limited to DDR4 memory. To upgrade to DDR5, you would need to perform a complete platform upgrade, which includes a new CPU, a new motherboard, and, of course, new DDR5 RAM. This can be a significant investment, making the "upgrade" more akin to building a new PC from scratch.
Counting the Pennies: DDR5 vs. DDR4 Pricing Realities
Early in DDR5's lifecycle, the price premium was steep, often making it a non-starter for anyone on a budget. However, as of 2025, the landscape has shifted considerably. DDR5 pricing is approaching parity with DDR4, especially for popular and performant kits around the 6000 MT/s mark.
For instance, a high-speed 2x16GB (32GB total) DDR5-6000 kit, which is often considered the sweet spot for performance and stability on current platforms, might only be marginally more expensive than an equivalent DDR4-3600 kit. The days of paying double for DDR5 are largely behind us.
However, if you're building on a tighter budget, DDR4 still holds the crown for affordability:
- Budget DDR5 kits (e.g., 2x8GB 4800 MT/s) are now typically only 15–20% more expensive than their DDR4 equivalents. This smaller gap makes entry-level DDR5 more palatable for new budget builds on compatible platforms.
- DDR4 remains significantly more cost-effective for true budget or mid-range builds. If you're upgrading an existing DDR4 system or building a new one on an LGA 1700 motherboard that supports DDR4, you can find excellent value in DDR4-3200 or DDR4-3600 kits. These speeds offer fantastic performance per dollar for most mainstream tasks and gaming.
- Price-sensitive users focused on general productivity or casual gaming will find DDR4 a solid and affordable choice that doesn't compromise much on the experience, especially if they are not running the latest CPU architectures that heavily benefit from DDR5.
The takeaway? While DDR5 is becoming more accessible, DDR4 still offers unparalleled value if minimizing cost is a top priority, particularly when factoring in potential CPU and motherboard savings on older platforms.
Building for Tomorrow: Is DDR5 Worth the Future-Proofing Premium?
"Future-proofing" is a term often thrown around in tech, sometimes with more hope than substance. With DDR5, however, there's genuine merit to the argument. DDR5 is unequivocally considered the future of system memory.
Major platforms and CPU architectures are rapidly transitioning away from DDR4. AMD's AM5 platform is DDR5-exclusive, and while Intel's LGA 1700 offers a choice, its successor platforms are expected to be DDR5-only. This means that if you're investing in a brand-new, high-end system today, opting for DDR5 places you firmly on the path of future hardware evolution.
Why does this matter?
- Emerging Workloads: Newer features and technologies, particularly those involving AI acceleration, machine learning, and increasingly high-bandwidth workloads (think about the ever-growing demand for real-time data processing and virtualization), will increasingly benefit from DDR5's capabilities. As software evolves to leverage these advancements, systems with DDR5 will be better positioned to handle them.
- Long-Term Compatibility: Building a PC with DDR5 today means you're investing in a platform that will likely be supported for the next 4–6 years or even longer. This ensures better compatibility with future software, operating system updates, and potential hardware upgrades (e.g., a CPU upgrade within the same socket generation). You won't be boxed out of new technologies simply because your memory standard is obsolete.
- Resale Value: A system built on a current, future-facing memory standard like DDR5 is likely to hold its value better over time, should you decide to sell or upgrade components down the line.
When Future-Proofing Isn't Enough:
It's important to temper expectations. Upgrading solely for future-proofing may not always justify the immediate cost, especially if: - You're already on a capable DDR4 platform that meets your current needs.
- Your budget is extremely tight, and the extra cost for DDR5 (and potentially a new CPU/motherboard) would mean sacrificing performance in other, more impactful components like a GPU.
- Your usage primarily involves light tasks or casual gaming that won't significantly benefit from DDR5's higher bandwidth in the short to medium term.
For most users building a new mid-to-high-end PC today, selecting a DDR5-compatible platform is a smart move that protects your investment and opens doors to future possibilities.
Beyond the Hype: Key Innovations Making DDR5 Tick
To truly appreciate DDR5, it's worth delving into some of the unsung heroes of its architecture that contribute to its superior performance and efficiency:
- Power Management Integrated Circuit (PMIC): Unlike DDR4, where power regulation was handled by the motherboard, DDR5 modules incorporate their own PMIC directly on the DIMM. This allows for more granular and efficient power delivery to the memory chips, reducing noise and improving stability. It's a key factor in DDR5's lower operating voltage and enhanced overclocking potential.
- XMP 3.0 (Extreme Memory Profile): Intel's XMP profiles make it incredibly easy to run your memory at its advertised speeds with a single BIOS setting. DDR5 introduces XMP 3.0, which allows for more customizable profiles (up to five profiles, three factory-set, and two user-reprogrammable). This provides greater flexibility for enthusiasts to fine-tune their memory's performance, allowing for easier experimentation with voltage, timing, and speed.
- Smaller Memory Banks for Greater Efficiency: DDR5 modules have more memory banks (32 banks in 8 groups compared to DDR4's 16 banks in 4 groups). These smaller banks allow for more operations to be queued simultaneously, leading to higher efficiency and reduced latency when accessing data.
- Increased Burst Length: DDR5 doubles the burst length from 8 (DDR4) to 16, and the prefetch buffer from 8n to 16n. This means that more data can be fetched in a single burst, further contributing to higher effective bandwidth.
These innovations, while complex, collectively contribute to DDR5's ability to offer higher speeds, greater stability, and better power efficiency, setting it apart from its predecessor.
Making the Smart Choice: Who Should Upgrade (or Stick)?
The decision between DDR4 and DDR5 hinges entirely on your current hardware, your budget, and your specific performance needs. There's no universal "better" option without context. Let's break it down by user profile:
You Should Absolutely Go DDR5 If:
- You're building a brand-new, high-end PC with an AMD Ryzen 7000 Series CPU (AM5 platform). This is a non-negotiable requirement for AM5.
- You're building a new Intel 12th/13th/14th Gen system and prioritizing future-proofing and peak performance. Choose a DDR5-compatible motherboard.
- You're a professional content creator, 3D artist, data scientist, or heavy multitasker. The increased bandwidth and capacity will directly translate to faster workflows and a more responsive system.
- You're an enthusiast gamer targeting extremely high frame rates (240Hz+) in CPU-bound esports titles or pairing with a 3D V-Cache CPU (like the 7800X3D). The subtle gains become more impactful here.
- Your budget allows for a complete platform upgrade (new CPU, motherboard, and RAM) and you want the latest technology.
You Should Stick with DDR4 (or consider it for new builds) If: - You're on an older platform (e.g., AMD AM4, Intel 11th Gen or older) and not planning a full system overhaul. Upgrading to DDR5 would mean a costly CPU/motherboard replacement that might not be justified for your needs.
- You're building a budget-conscious or mid-range PC and every dollar counts. DDR4 offers fantastic performance-per-dollar, freeing up funds for a better GPU or SSD.
- Your primary use is general productivity, web browsing, office work, or casual gaming. DDR4-3200 or DDR4-3600 provides more than enough performance for these tasks without the premium.
- You already own a capable DDR4 system and don't feel performance bottlenecks in your current tasks. "If it ain't broke, don't fix it" applies here. Wait for your next major upgrade cycle.
- You're building a new Intel LGA 1700 system and find a DDR4 motherboard/RAM combo significantly cheaper. For many, the slight performance difference might not justify the cost hike.
Common Questions, Clear Answers
Let's tackle some frequently asked questions that often arise in the DDR4 vs. DDR5 debate:
Q: Will DDR5 make my games run twice as fast?
A: No. While DDR5 offers performance gains, they are generally not a 2x increase in frame rates for most games. Gains are often marginal in GPU-bound scenarios and more noticeable in CPU-bound situations or with specific CPU architectures (like AMD's 3D V-Cache).
Q: Can I mix DDR4 and DDR5 memory on the same motherboard?
A: Absolutely not. Motherboards are designed to support either DDR4 or DDR5, but never both simultaneously. Trying to install the wrong type of RAM will physically not work and could potentially damage components.
Q: Is DDR4 completely obsolete now?
A: No, far from it. DDR4 remains a highly capable and cost-effective memory standard. For many users, particularly those on existing platforms or building on a budget, DDR4 offers excellent performance and value. It will likely remain relevant for several years for mainstream computing.
Q: What does MT/s mean, and why is it important for RAM?
A: MT/s stands for "MegaTransfers per second." It's a measure of how many data transfers occur per second. Higher MT/s generally means faster raw memory speed, which contributes to higher bandwidth and quicker data access for your CPU. When comparing DDR4 and DDR5, the MT/s numbers are often the first performance metric you'll see.
Q: Does RAM speed matter more than quantity (GB)?
A: Both matter! Think of it like a highway: quantity (GB) is the number of lanes, and speed (MT/s) is the speed limit. You need enough lanes to hold all your data (e.g., 16GB for gaming, 32GB+ for professional work), but you also want a high speed limit to move that data quickly. For most users, 16GB is the minimum, and 32GB is the sweet spot. After you have enough quantity, faster speeds offer diminishing returns unless you have specific, demanding workloads.
Your Next Move: Equipping Your Rig for Peak Performance
The journey from DDR4 to DDR5 isn't a simple upgrade; it's a generational leap that redefines memory architecture. While DDR5 is undeniably the path forward, promising higher bandwidth, greater efficiency, and a clearer future, DDR4 continues to offer excellent value and performance for a vast segment of users.
Ultimately, your decision shouldn't be driven by hype, but by an honest assessment of your current hardware, your budget, and what you genuinely need your PC to accomplish. If you're building a new, high-performance system today, particularly on AMD's latest platform, DDR5 is the natural and necessary choice. If you're on a tighter budget, or simply looking to refresh an existing DDR4 system, sticking with DDR4 will still deliver a powerful and satisfying experience.
Whichever you choose, ensure it aligns with your specific goals. Invest smart, build confident, and enjoy the power of modern computing.